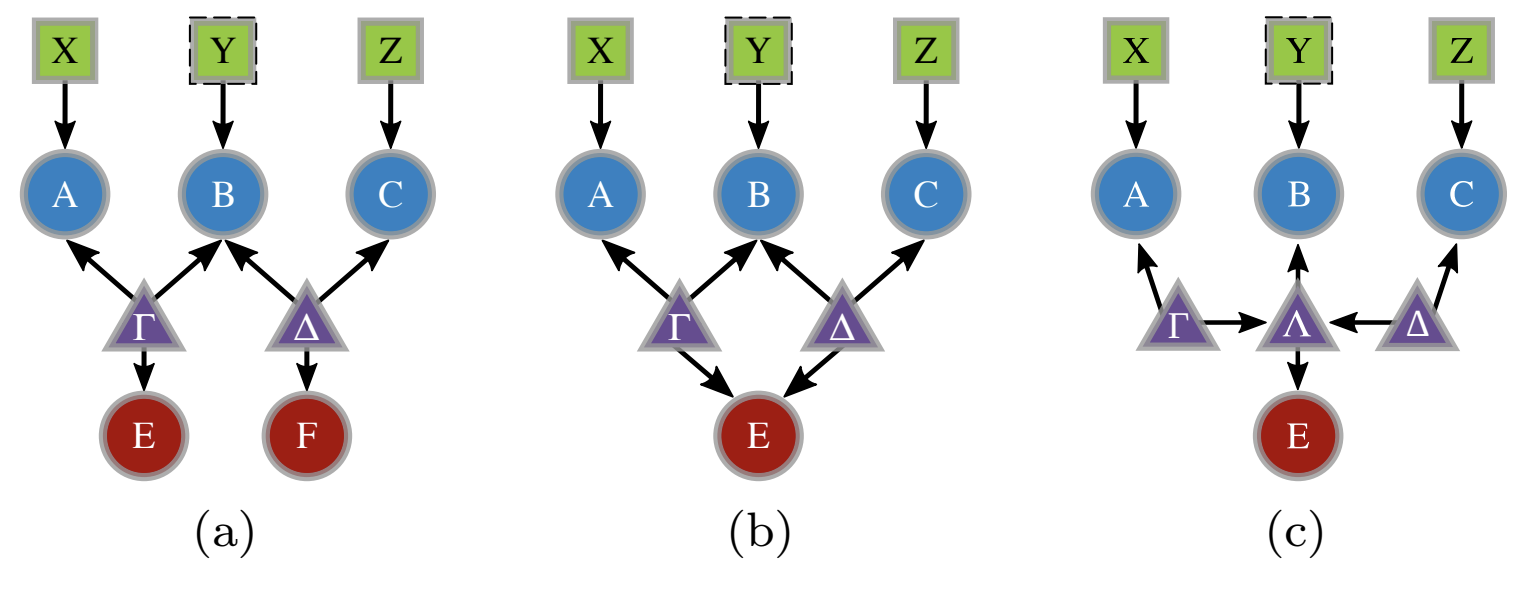
Randomness certification is a foundational and practical aspect of quantum information science, essential for securing quantum communication protocols. Traditionally, these protocols have been implemented and validated with a single entanglement source, as in the paradigmatic Bell scenario. However, advancing these protocols to support more complex configurations involving multiple entanglement sources is key to building robust architectures and realizing large-scale quantum networks. In this work, we show how to certify randomness in an entanglement-teleportation experiment, the building block of a quantum repeater displaying two independent sources of entanglement. Utilizing the scalar extension method, we address the challenge posed by the non-convexity of the correlation set, providing effective bounds on an eavesdropper’s knowledge of the shared secret bits. Our theoretical model characterizes the certifiable randomness within the network and is validated through the analysis of experimental data from a photonic quantum network.
“Experimental randomness certification in a quantum network with independent sources”